#hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
GTBank Confirms Attempt To Compromise Website, Assures Customers No Data Breach
Guaranty Trust Bank (GTB) Ltd says there were attempts to compromise its website domain but customers’ data were not affected. On Wednesday, reports circulated that there was a compromise on the domain address of GTBank by suspected cyber criminals. The attackers were said to have created another hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) layer of the website in an apparent ploy to steal customers’ data…
0 notes
Text
Securing Your Website: Best Practices for Web Developers
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, website security has become a paramount concern for businesses and individuals alike. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, it is crucial for web developers to adopt robust security measures to safeguard their websites and the sensitive data they handle. In this article, we'll delve into the best practices that web developers can implement to enhance the security of their websites and protect against potential threats.
Introduction
In today's interconnected world, websites serve as the digital storefront for businesses, making them vulnerable targets for cyber attacks. From data breaches to malware infections, the consequences of a security breach can be severe, ranging from financial loss to damage to reputation. Therefore, prioritizing website security is essential for maintaining the trust and confidence of users.
Understanding Website Security
Before diving into best practices, it's crucial to understand the importance of website security and the common threats faced by websites. Website security encompasses measures taken to protect websites from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Common threats include malware infections, phishing attacks, SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and brute force attacks.
Best Practices for Web Developers
Keeping Software Updated
One of the most fundamental steps in website security is keeping all software, including the content management system (CMS), plugins, and server software, updated with the latest security patches and fixes. Outdated software is often targeted by attackers due to known vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
Implementing HTTPS
Implementing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data transmitted between the website and its users, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. HTTPS not only protects sensitive information but also boosts trust among visitors, as indicated by the padlock icon in the browser's address bar.
Using Strong Authentication Methods
Implementing strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and CAPTCHA, adds an extra layer of security to user accounts. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their mobile device, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Securing Against SQL Injection Attacks
SQL injection attacks occur when malicious actors exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to execute arbitrary SQL commands. Web developers can prevent SQL injection attacks by using parameterized queries and input validation to sanitize user inputs effectively.
Protecting Sensitive Data
It's essential to employ encryption techniques to protect sensitive data, such as passwords, credit card information, and personal details, stored on the website's servers. Encrypting data at rest and in transit mitigates the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the website's infrastructure and codebase. Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code reviews enable web developers to proactively address security issues before they are exploited by attackers.
Choosing a Secure Hosting Provider
Selecting a reputable and secure hosting provider is critical for ensuring the overall security of your website. When evaluating hosting providers, consider factors such as security features, reliability, scalability, and customer support.
Evaluating Security Features
Choose a hosting provider that offers robust security features, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), malware scanning, and DDoS protection. These features help protect your website from various cyber threats and ensure continuous uptime.
Ensuring Regular Backups
Regularly backing up your website's data is essential for mitigating the impact of security incidents, such as data breaches or website compromises. Choose a hosting provider that offers automated backup solutions and store backups securely offsite.
Customer Support and Response to Security Incidents
Opt for a hosting provider that provides responsive customer support and has established protocols for handling security incidents. In the event of a security breach or downtime, prompt assistance from the hosting provider can minimize the impact on your website and business operations.
Implementing Firewall Protection
Firewalls act as a barrier between your website and external threats, filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. There are several types of firewalls, including network firewalls, web application firewalls (WAF), and host-based firewalls.
Configuring and Maintaining Firewalls
Properly configuring and maintaining firewalls is crucial for effective security. Define firewall rules based on the principle of least privilege, regularly update firewall configurations to reflect changes in the website's infrastructure, and monitor firewall logs for suspicious activity.
Educating Users about Security
In addition to implementing technical measures, educating users about security best practices is essential for enhancing overall website security. Provide users with resources, such as security guidelines, tips for creating strong passwords, and information about common phishing scams.
Importance of User Awareness
Users play a significant role in maintaining website security, as they are often the targets of social engineering attacks. By raising awareness about potential threats and providing guidance on how to recognize and respond to them, web developers can empower users to stay vigilant online.
Providing Training and Resources
Offer training sessions and educational materials to help users understand the importance of security and how to protect themselves while using the website. Regularly communicate updates and reminders about security practices to reinforce good habits.
Monitoring and Responding to Security Incidents
Despite taking preventive measures, security incidents may still occur. Establishing robust monitoring systems and incident response protocols enables web developers to detect and respond to security threats in a timely manner.
Setting Up Monitoring Tools
Utilize monitoring tools, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and website monitoring services, to detect abnormal behavior and potential security breaches. Configure alerts to notify you of suspicious activity promptly.
Establishing Incident Response Protocols
Develop comprehensive incident response plans that outline roles, responsibilities, and procedures for responding to security incidents. Establish clear communication channels and escalation paths to coordinate responses effectively and minimize the impact of security breaches.
Securing your website requires a proactive approach that involves implementing a combination of technical measures, choosing a secure hosting provider, educating users about security best practices, and establishing robust monitoring and incident response protocols. By following these best practices, web developers can mitigate the risk of security breaches and safeguard their websites and the sensitive data they handle.
#website security has become a paramount concern for businesses and individuals alike. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated#it is crucial for web developers to adopt robust security measures to safeguard their websites and the sensitive data they handle. In this#we'll delve into the best practices that web developers can implement to enhance the security of their websites and protect against potenti#Introduction#In today's interconnected world#websites serve as the digital storefront for businesses#making them vulnerable targets for cyber attacks. From data breaches to malware infections#the consequences of a security breach can be severe#ranging from financial loss to damage to reputation. Therefore#prioritizing website security is essential for maintaining the trust and confidence of users.#Understanding Website Security#Before diving into best practices#it's crucial to understand the importance of website security and the common threats faced by websites. Website security encompasses measur#phishing attacks#SQL injection#cross-site scripting (XSS)#and brute force attacks.#Best Practices for Web Developers#Keeping Software Updated#One of the most fundamental steps in website security is keeping all software#including the content management system (CMS)#plugins#and server software#updated with the latest security patches and fixes. Outdated software is often targeted by attackers due to known vulnerabilities that can#Implementing HTTPS#Implementing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data transmitted between the website and its users#ensuring confidentiality and integrity. HTTPS not only protects sensitive information but also boosts trust among visitors#as indicated by the padlock icon in the browser's address bar.#Using Strong Authentication Methods#Implementing strong authentication methods
0 notes
Text
XHR stands for "XML HTTP Request", where XML is the "eXtensible Markup Language" and HTTP is the "Hypertext Transfer Protocol", so the full expansion of XHR is "extensible markup language hypertext transfer protocol request", so those 3 letters expand to 56 letters (62 with spaces), and this got me wondering, there must be acronyms or initialisms with an even greater ratio of "expanded length"/"unexpanded length", but apart from recursive acronyms I can't think of longer examples.
Can anyone else think of any?
#I thought maybe some joke acronyms would work#but I think it has to be another initialism where some letters stand for other initialisms in order to break 56/3
270 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are HTTP requests?
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) requests is one of the most common ways information is communicated between clients and servers on the internet. A client will go to the server to get resources or perform an action via a HTTP request.
HTTP requests follow a standard structure:
Request line - the request line specifies what HTTP method is being used (more on that below), the endpoint (a URL/URI, a server location on the web) that the request is being sent to. And what version of HTTP is being used.
Headers - Additional information that needs passing between client and server (cookies, authentication, OS version, etc)
Message body - data to be passed as part of the request.
HTTP has set methods which can be used for requests, they're used for different purposes.
HTTP methods
GET - used to retrieve data from a server
HEAD - is similar to get but has no body, it's usually used to assess if an API is currently available.
POST - used to send information to the server to create or update a resource using information stored in the body of the HTTP request.
PUT - Updates or creates a resource. PUT requests are idempotent, the results of them stay the same no matter how many times it's called.
DELETE - used to delete a resource from a server.
PATCH - used to update information on the server with a partial modification. E.g. updating only the title of an article.
TRACE - used as a loop back test, usually used for debugging and diagnostics of APIs
CONNECT - creates a tunnel connection to a server specified by the URL provider.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Remembered this and thought I'd post my virtual safety tips here so it's easier to pass around if needed.
here is some base things to know if someone is scamming you:
Did they suddenly get into contact with no sign of mutual interests or knowledge of each other?
Are they suddenly asking too many questions? (especially personal ones)
Did they suddenly tell you about something big that happened and you are involved despite no knowledge? <- base scam right there
Discord's official E-Mail is: <[email protected]>
They are trying anything they can to get you OUT of discord
How to check if a screenshot is viable or not:
The layout is the same as what it claims to be, check for the details such as profile picture, date, names, lines, colors
Remember that it's easy to fake messages like discord, twitter, instagram etc. there's websites for it that create fake posts/messages etc.
What to do when you suspect a scam/Someone is asking for information: Are they asking about these things...
Your daily routine?
Your schedule?
Your friends/relatives/Family?
If you have a lover/bf/gf/etc.?
Your age?
Where you are from
Other possible personal information
then don't answer them directly, usually people leave you alone when you start questioning their intentions, ask them why they need this info, question it why, why, why, if they have VALID reasons to know, they will be able to explain, if they don't then they will circle around and eventually get mad at you and leave or you can leave because angry people are hard to talk to.
Are they asking you to move somewhere else? (like e-mails, snapchat, instagram, twitter, etc.)
Then check the URL they sent. SAFE URL's go like this: "HttpS" the S stands for safe, http stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, the S adds safety to the site (nowdays most should be safe)
Check first word before any / this is the general website name, if you remove everything after the / and the symbol itself, you should be on the HOMEPAGE anything after / is a subfolder which means that it should specify where exactly the url is leading to like in the example: "hc/en-us/articles/218410947-I-forgot-my-Password-Where-can-I-set-a-new-one" which basically means that it was in the HC folder under "english articles" number 218... etc The LAST sentence after the last / is the name of the page you are currently on.
This is the general layout of a URL, phishing websites are very easy to make but cheap ones are easily detectable because their URLs seem off, incoherent or even absurd. Generally the website can't get anything else from you other than your IP, which is basically your location and your pc's workshop name, it isn't that dangerous, games often use IP's to share multiplayer etc.
What IS dangerous is when the website demands you to log in or asks for personal information. Never put in any information when you didn't check for the liability of the URL and know on point exact what is going on and got a thumbs up from friends if you are suspicious. better ask more questions than not!
stay safe on the internet everyone!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
World Wide Web
The internet was created to give the US military a communication system that could survive a nuclear war. The idea was to have an interconnected network of computers without hardline routing. Instead it was handled by variable heuristics. This means that even if half of the nodes were destroyed, the system could find a way to route along different paths and still, eventually, reach it's destination.
It was a brilliant form of asynchronous communication.
Academia had created it, and quickly found great use in networked communication and remote data processing.
And now we use it to view porn. So, what happened?
The World Wide Web. Before the WWW, you had to know the IP address of your friend's computer, be given permission, and then log into his bulletin board service.
The World Wide Web was a system of protocols that created a public internet front. ANY person could find it through HyperText Transfer Protocol, use a public log-in, and access the web site. The HTTP was designed to be crawled by search engines, allowing them to effectively index the entirety of the public-facing internet.
One of the first real search engines was call WebCrawler, because it - crawled - the HTTP of the WWW.
They would load page, then open and index every - single - hyperlink contained in the document, storing and indexing meta tags.
We also ended up with MetaCrawler, that would index multiple other search engines, allowing it to provide a far more comprehensive system of results.
Nowadays, most search engines are meta crawlers, and because of the prominence of Google in searching, Google results are over weighted, meaning that there is almost no way to escape the dogmatism of Google's biased search algorithms.
And the reason we use it for porn is that this was the first viable online business plan.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
HTTP to HTTPS: The Incorporation of the Secure Sockets Layer TLS

What is HTTP vs. HTTPS? HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the basic protocol that enables communication between your browser and the server hosting the website. It has been the foundation of the web since its inception. However, HTTP lacks encryption, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks like eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks, and data tampering.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is an upgraded version of HTTP that integrates SSL/TLS encryption, ensuring a secure transfer of data between a user’s browser and the web server. HTTPS protects sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, and personal information, making it essential for websites that collect user data.
Learn more: What is HTTP vs. HTTPS? HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the basic protocol that enables communication between your browser and the server hosting the website. It has been the foundation of the web since its inception. However, HTTP lacks encryption, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks like eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks, and data tampering.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is an upgraded version of HTTP that integrates SSL/TLS encryption, ensuring a secure transfer of data between a user’s browser and the web server. HTTPS protects sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, and personal information, making it essential for websites that collect user data.
Learn more: https://www.ayansujon.com/http-to-https-the-incorporation-of-the-secure-sockets-layer-tls/
#wordpress#sslcertificates#sslcertificateforwebsite#wordpresssecurity#wordpresssecurityblog#wordpresssecurityexpert
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
JODI.ORG
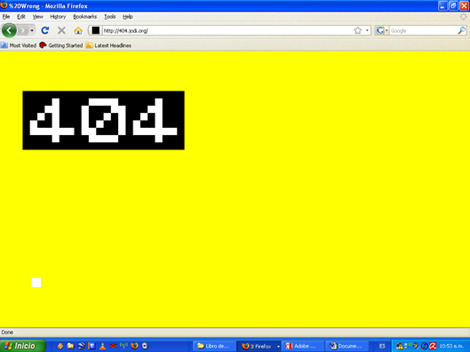
Es un dúo de artistas de Internet formado por Joan Heemskerk de Holanda y Dirk Paesmans de Bélgica. Considerados artistas claves del Net.art.
Se consideran muy importantes en la rama del Net.art. Cada uno de sus trabajos artísticos consiste en una página web en la cual se encuentra alterada la estructura y su código interno. Este cambio no es al azar y tiene una finalidad estética. Se trata de mostrar la fragilidad de este mundo virtual y cómo un ligero error de programación puedo volcar todo un sistema como lo es una página web.
Sus finalidades es explorar el ordenador para luego reflejarlo o plasmarlo en la red como una obra de arte. Para ellos, es un gran honor que miles de personas puedan ver sus obras a través de sus pantallas. En este caso, elegí la obra “20%Wrong”, la cual es una pagina en la que aparecerán los números “404” el cual es un error común cuando un ordenador no encuentra una” URL o HTML”. Pero en este caso, esta página fue creada totalmente adrede, y cada vez que cargas la página, cambian de color. (Amarillo, turquesa, rosa, pero jamás blanco.)
En mi opinión acerca del Net.art, me parece un estilo de arte bastante curioso, pero a la vez me fascina el hecho de que las personas seamos capaces de hacer arte a partir de errores informáticos o códigos y como lo comparten en miles de redes sociales para que otras personas sean capaces de apreciarlo. Es algo triste, que seguramente hoy en día la gente ya no haga este tipo de cosas, o muy pocas.
El color es plano, el número 404 está en el extremo superior izquierdo (números blancos sobre un rectángulo negro). El Error 404 es una de las manifestaciones de la lista de códigos de protocolo HTTP ( hypertext transfer protocol, o protocolo de transferencia de hipertexto) que significa: File not found.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are both protocols used for transmitting data over the internet. However, they differ significantly in terms of security, data integrity, and privacy. This analysis aims to compare and contrast HTTP and HTTPS, highlighting their key differences, advantages, and disadvantages.
1. Security:
HTTP: HTTP operates over plaintext, meaning data sent between the client and server is not encrypted. This makes it vulnerable to interception, manipulation, and eavesdropping attacks. Any data transmitted via HTTP can be easily accessed by malicious actors.
HTTPS: HTTPS encrypts data using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols, providing a secure connection between the client and server. This encryption ensures that even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable to unauthorized parties, significantly enhancing security.
2. Data Integrity:
HTTP: Since data transmitted over HTTP is not encrypted, there's no built-in mechanism to verify its integrity. This makes HTTP susceptible to data tampering during transmission. Any alterations made to the data during transit may go unnoticed.
HTTPS: HTTPS ensures data integrity by employing cryptographic algorithms to verify that the transmitted data remains unchanged during transit. Any attempt to tamper with the data will result in the receiver being alerted to the integrity breach.
3. Authentication:
HTTP: HTTP does not provide any mechanisms for server authentication, making it vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks. Clients cannot be certain that they are communicating with the intended server, as there is no way to verify its authenticity.
HTTPS: HTTPS authenticates the server's identity using digital certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). This authentication process ensures that clients can trust the server they are communicating with, mitigating the risk of impersonation and unauthorized access.
4. Privacy:
HTTP: Since HTTP transmissions are unencrypted, sensitive information such as login credentials, personal data, and financial details are transmitted in plaintext, leaving users vulnerable to privacy breaches.
HTTPS: HTTPS encrypts sensitive data, safeguarding user privacy and preventing unauthorized parties from intercepting and accessing confidential information.
5. Performance:
HTTP: HTTP typically offers faster performance compared to HTTPS, as there is no overhead associated with encryption and decryption processes. This can be advantageous for websites that prioritize speed over security.
HTTPS: HTTPS may introduce a slight performance overhead due to the encryption and decryption processes involved. However, advancements in encryption algorithms and hardware acceleration have minimized this overhead, making the difference in performance negligible for most users.
#seoexpertshankarhalder #seospecialistshankarhalder #shankarhalder #seoservice
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role Of HTTPS In SEO Secure Your Accounting Website
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital security and online presence, the importance of securing your accounting website with HTTPS cannot be overstated. HTTPS, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is not just a technical jargon—it’s a critical element that significantly impacts your website’s search engine optimization (SEO) and, ultimately, the trustworthiness of your accounting firm. Let’s delve into the reasons why HTTPS is essential and how it can play a pivotal role in securing and enhancing your online presence.
Security Assurance:
HTTPS provides a secure and encrypted connection between the user’s browser and your accounting website’s server. This encryption ensures that sensitive data, such as client information and financial details, remains private and protected from potential cyber threats. In an era where data breaches are a real concern, having a secure website builds trust with your clients and safeguards your reputation.
Search Engine Ranking Boost:
Search engines, especially Google, prioritize user safety and privacy. As a result, websites with HTTPS receive a ranking boost in search results. Google considers HTTPS as a ranking signal, meaning that secure websites are more likely to appear higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This boost can contribute to increased visibility and, consequently, more traffic to your accounting website.
Browser Security Warnings:
Modern web browsers, such as Google Chrome, have started to label websites without HTTPS as “Not Secure.” This warning can deter potential clients from staying on your website, causing them to abandon it before exploring your accounting services. By adopting HTTPS, you eliminate these warnings and create a seamless and secure browsing experience for your visitors.
User Trust and Confidence:
Clients seeking accounting services are likely to share sensitive information on your website. The sight of the padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, indicating a secure connection, instills confidence in users. This trust is invaluable, especially in a profession where confidentiality and reliability are paramount. The implementation of HTTPS assures your clients that their data is handled with the utmost care.
Compliance with Industry Standards:
As the digital landscape evolves, compliance with industry standards becomes increasingly important. Many regulatory bodies and industry associations require secure connections for websites handling financial or personal information. Adopting HTTPS ensures that your accounting website meets these standards, positioning your firm as a responsible and compliant entity.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the adoption of HTTPS is not merely a technical formality; it is a strategic move that influences the success of your accounting firm online. The secure connection it provides not only protects sensitive data but also positively impacts your search engine rankings, user trust, and overall online reputation. With the expertise of an SEO agency for accountants, prioritizing the security of your website becomes a seamless process, reinforcing your commitment to digital trust and setting your practice apart in the competitive online landscape.
By prioritizing the security of your website, you’re not only complying with industry standards but also sending a powerful message to your clients—that their privacy and security are at the forefront of your priorities.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ensuring Robust Security for Your Blogspot Blog

In today's digital landscape, online security is of paramount importance, and bloggers must take proactive steps to safeguard their Blogspot blogs from potential threats. While Blogspot, the popular blogging platform, provides several built-in security features, it's essential for bloggers to implement additional measures to protect their blogs and maintain the trust of their readers. If you want to know about Getting Started with Blogspot, Visit My Article. This article explores various strategies and best practices for enhancing the security of your Blogspot blog.
Keep Your Software Updated
Regularly updating your Blogspot software is vital for ensuring the security of your blog. Google, the owner of Blogspot, continually releases security patches and updates to address any vulnerabilities. Enable automatic updates or manually check for updates to ensure that your blog is running on the latest version of Blogspot.
Secure Your Login Credentials
A strong and unique password is the first line of defense against unauthorized access to your Blogspot account. Avoid using easily guessable passwords and consider utilizing a password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords. Additionally, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for an extra layer of security, requiring both your password and a verification code for login.
Enable HTTPS
Securing your blog with HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is crucial for protecting sensitive information transmitted between your blog and its visitors. Blogspot offers free HTTPS encryption for custom domains, ensuring that data exchanged between users and your blog remains confidential. To enable HTTPS, go to the "Settings" section of your Blogspot dashboard and select "HTTPS" from the "HTTPS Availability" dropdown menu.
Regularly Backup Your Blog
Performing regular backups of your Blogspot blog is essential to protect your data in the event of a security breach or accidental data loss. Blogspot provides an option to export your entire blog, including posts, comments, and settings, as an XML file. Set a schedule for periodic backups and store them securely, either locally or using a cloud storage service.
Monitor and Manage User Permissions
If you collaborate with others on your Blogspot blog, carefully manage user permissions to restrict access to sensitive areas. Assign roles with appropriate access levels to contributors, ensuring they only have the necessary permissions for their tasks. Regularly review user accounts and remove any inactive or unnecessary users to minimize potential security risks.
Be Mindful of Third-Party Widgets and Plugins
While third-party widgets and plugins can enhance the functionality and appearance of your Blogspot blog, they can also pose security risks if not carefully vetted. Only install widgets and plugins from reputable sources, and regularly update them to ensure you have the latest security patches. Remove any unused or outdated plugins to reduce potential vulnerabilities.
Protect Against Comment Spam and Malicious Links
Blogspot has built-in features to combat comment spam, but it's essential to keep these settings properly configured. Enable comment moderation, captchas, and anti-spam filters to prevent spam comments from appearing on your blog. Additionally, exercise caution when approving comments containing links, as they may direct users to malicious websites. Avoid publishing comments that appear suspicious or contain unverified links.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
2024 Tumblr Top 10
1. 28,490 notes - Jul 1 2024
It always gets me that the name "Gandalf" literally just means "Wand-Elf" or "Stick-Elf". I'm imagining old Gondorians just...
2. 12,136 notes - Aug 27 2024
My T-shirt with the entire text of Borges' theoretical Library of Babel is raising a lot of questions already answered by the...
3. 7,696 notes - Dec 15 2024
I don't know who needs to hear this, but it's time to take your 12 partridges, 22 turtle doves, 30 french hens, 36 calling...
4. 1,888 notes - Mar 22 2024
Hmmm. A finger is a unit of volume, as in "two fingers of whiskey". A hand is a unit of length (most commonly the heights of...
5. 981 notes - Jul 5 2024
Corrections
6. 494 notes - Apr 24 2024

7. 428 notes - Apr 28 2024

8. 270 notes - Apr 11 2024
XHR stands for "XML HTTP Request", where XML is the "eXtensible Markup Language" and HTTP is the "Hypertext Transfer Protocol",...
9. 247 notes - Mar 27 2024

10. 168 notes - Jul 15 2024
POLL RACE 🐛 A Walrus Secret Third Thing Vanilla Extract I don't know / I'm bald / Some other infinitely nuanced answer Other...
Created by TumblrTop10
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Defines a Truly Secure Website?

In today's digital landscape, a website is often the front door to a business, a personal brand, or vital information. With cyber threats constantly evolving, the question isn't just "Is my website online?" but "Is my website truly secure?" Many users look for the padlock icon and "HTTPS" in the address bar and breathe a sigh of relief. While essential, that green lock is merely the beginning of true website security.
HTTPS signifies that the connection between your browser and the website's server is encrypted, protecting data in transit. But a truly secure website goes far beyond encrypting data between two points. It's built on a multi-layered defense strategy, addressing vulnerabilities at every level of the application and infrastructure.
So, what are the characteristics of a website you can genuinely trust?
1. Always Uses HTTPS with Strong TLS Protocols
This is the foundational layer, but its proper implementation is crucial.
What it is: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the communication between the user's browser and the website's server using TLS (Transport Layer Security, the modern successor to SSL) certificates.
Why it's essential: It prevents eavesdropping, tampering, and message forgery, ensuring that the data you send (like login credentials or credit card numbers) and receive remains private and integral. Modern browsers flag sites without HTTPS as "Not Secure." Crucially, truly secure websites use strong, up-to-date TLS versions (like TLS 1.2 or 1.3), not older, vulnerable ones.
2. Robust Input Validation and Output Encoding
These are fundamental defenses against some of the most common web attacks.
Input Validation: Every piece of data a user submits (forms, search queries, URLs) must be strictly validated before the server processes it. This prevents attackers from injecting malicious code (e.g., SQL Injection, Command Injection) that could manipulate the database or execute commands on the server.
Output Encoding: Any data retrieved from a database or user input that is displayed back on the website must be properly encoded. This prevents Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks, where malicious scripts could be executed in a user's browser, stealing cookies or defacing the site.
3. Strong Authentication & Authorization Mechanisms
Security starts with knowing who is accessing your site and what they are allowed to do.
Authentication:
Strong Password Policies: Enforce minimum length, complexity (mix of characters), and disallow common or previously breached passwords.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Offer and ideally mandate MFA for all user accounts, especially administrative ones. This adds a critical layer of security beyond just a password.
Secure Session Management: Use secure, short-lived session tokens, implement proper session timeouts, and regenerate session IDs upon privilege escalation to prevent session hijacking.
Authorization: Implement the principle of least privilege. Users should only have access to the data and functionalities strictly necessary for their role. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is key here, ensuring a customer can't access admin features, for instance.
4. Regular Security Updates & Patch Management
Software is complex, and vulnerabilities are constantly discovered.
Continuous Patching: The website's underlying operating system, web server software (e.g., Apache, Nginx), Content Management System (CMS) like WordPress or Drupal, plugins, themes, and all third-party libraries must be kept up-to-date with the latest security patches.
Why it's essential: Unpatched vulnerabilities are a common entry point for attackers. A truly secure website has a rigorous system for identifying and applying updates swiftly.
5. Comprehensive Error Handling & Logging
What happens when things go wrong, or suspicious activity occurs?
Generic Error Messages: Error messages should be generic and not reveal sensitive system information (e.g., database connection strings, file paths, or specific error codes) that attackers could use to map your system.
Robust Logging: All security-relevant events – failed login attempts, successful logins, administrative actions, suspicious requests, and critical system events – should be logged. These logs should be stored securely, centrally, and monitored in real-time by a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system for anomalies and potential attacks.
6. Secure Development Practices (SDL)
Security isn't an afterthought; it's built in from the ground up.
Security by Design: A truly secure website is born from a development process where security considerations are embedded at every stage – from initial design and architecture to coding, testing, and deployment. This is known as a Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL).
Code Reviews & Testing: Regular security code reviews, static application security testing (SAST), and dynamic application security testing (DAST) are performed to identify and fix vulnerabilities before the code ever goes live.
7. Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF acts as a protective shield for your website.
What it does: It monitors and filters HTTP traffic between the web application and the internet. It can detect and block common web-based attacks (like SQL injection, XSS, DDoS, brute-force attempts) before they reach the application.
Why it helps: It provides an additional layer of defense, especially useful for mitigating new threats before a patch is available or for protecting against known vulnerabilities.
8. Data Encryption at Rest
While HTTPS encrypts data in transit, data stored on servers needs protection too.
Sensitive Data Encryption: Databases, file systems, and backups containing sensitive user information (passwords, PII, financial data) should be encrypted.
Why it's important: Even if an attacker manages to breach your server and access the underlying storage, the data remains unreadable without the encryption key, significantly mitigating the impact of a breach.
9. Regular Security Audits & Penetration Testing
Proactive testing is key to finding weaknesses before malicious actors do.
Vulnerability Scanning: Automated tools scan your website for known vulnerabilities.
Penetration Testing (Pen-Testing): Ethical hackers simulate real-world attacks to exploit vulnerabilities, test your defenses, and assess your overall security posture. These should be conducted regularly and after significant changes to the website.
10. Clear Privacy Policy & Data Handling Transparency
While not a strictly technical security feature, transparency builds user trust and demonstrates responsible data stewardship.
What it includes: A clear, easily accessible privacy policy explaining what data is collected, why it's collected, how it's used, how it's protected, and who it's shared with.
Why it matters: It shows commitment to data security and respects user privacy, a fundamental aspect of a truly trustworthy online presence.
A truly secure website is not a static state achieved by checking a few boxes. It's a continuous commitment to vigilance, proactive measures, and a deep understanding that security is an ongoing process involving people, technology, and robust policies. In a world where digital trust is paramount, building and maintaining a genuinely secure website is an investment that pays dividends in reputation, customer loyalty, and business continuity.
0 notes
Text
Some information technology acronyms
RAM = Random Access Memory
SIM = Subscriber Identity Module
SMS = Short Message Service
USB = Universal Serial Bus
WiFi = Wireless Fidelity
VLAN = Virtual Local Area Network
VPN = Virtual Private Network
HTTPS = HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure
WWW = World Wide Web
URL = Uniform Resource Locator
JPEG = Joint Photographic Experts Group
GIF = Graphics Interchange Format
PDF = Portable Document Format
CD = Compact Disc
DVD = Digital Video Disc
GPS = Global Positioning System
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hướng dẫn sửa lỗi Mixed Content trên WordPress
Hướng dẫn sửa lỗi Mixed Content trên WordPress #WordPress #HTTPS #MixedContent #LỗiWebsite #BảoMậtWebsite Lỗi Mixed Content xảy ra khi một trang web WordPress, mặc dù được truy cập thông qua giao thức bảo mật HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), lại vẫn tải một số tài nguyên (như hình ảnh, tập tin CSS, JavaScript) thông qua giao thức HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) không an toàn. Điều…
0 notes
Text
Securing Your Web Application: Key Strategies for Protection

As the digital landscape continues to evolve, securing web applications has become more important than ever. With the increasing prevalence of cyberattacks, data breaches, and security vulnerabilities, ensuring your web application is protected should be a top priority. Whether you're building a new application or maintaining an existing one, it's critical to take proactive steps to safeguard user data and ensure the security of your platform. For businesses looking to create secure applications, enlisting web application development services can provide the expertise needed to implement the best security practices from the ground up.
Here, we’ll explore some key strategies to help secure your web application and protect it from potential threats.
1. Use HTTPS for Secure Communication
One of the most fundamental steps in securing your web application is ensuring that all communications between users and your servers are encrypted. This is achieved by implementing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure). HTTPS uses SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt data, preventing hackers from intercepting sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal data, or payment details.
Without HTTPS, data is transmitted in plain text, making it vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks. Make sure that every page of your web application, especially login, registration, and payment pages, uses HTTPS to safeguard your users' information.
2. Implement Strong Authentication and Authorization
Authentication and authorization are essential for verifying user identities and controlling access to your web application’s resources. It’s crucial to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide multiple forms of identity verification before granting access.
Additionally, ensure your application follows the principle of least privilege (PoLP) — only allowing users to access resources they absolutely need. This limits the impact of a potential security breach, as even if a hacker gains access to one part of the application, they won’t be able to access all user data or resources.
3. Sanitize Input to Prevent SQL Injection
SQL injection remains one of the most common security vulnerabilities in web applications. This occurs when an attacker manipulates input fields to inject malicious SQL code into your application’s database. To prevent this, always sanitize and validate user input, using parameterized queries and prepared statements when interacting with your database.
Additionally, use input validation libraries and frameworks that automatically escape malicious characters. Never trust user input, and treat all inputs as potentially harmful.
4. Keep Your Software Up to Date
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to secure your web application is by keeping all software up to date. This includes your web application framework, libraries, plugins, and any third-party services you use. Software vendors often release patches and updates to fix security vulnerabilities, so it’s essential to install these updates promptly.
Neglecting to update your software can leave your application open to known exploits that attackers could easily take advantage of. Setting up automated update systems or regularly reviewing available updates can help ensure your application stays secure.
5. Implement Proper Session Management
Session management is another crucial element in securing your web application. Ensure that user sessions are securely managed and expired after a reasonable period of inactivity. Use secure session tokens, which are harder to predict, and store them in a secure location, such as HTTP-only cookies, to reduce the risk of session hijacking.
You should also consider implementing session logging and monitoring to detect unusual activity, such as multiple failed login attempts or sessions accessed from unusual locations. This allows you to act quickly and prevent unauthorized access.
6. Protect Against Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is another common vulnerability in web applications, where attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. These scripts can steal session cookies, perform actions on behalf of users, or redirect them to malicious websites.
To protect your application from XSS attacks, ensure you sanitize and escape any user-generated content before displaying it. This includes using Content Security Policy (CSP) headers to prevent untrusted scripts from executing and implementing strict input validation to block dangerous scripts.
7. Utilize Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a security system that monitors and filters HTTP requests to and from a web application. WAFs can help protect your application from a variety of threats, including SQL injection, XSS, and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
WAFs work by examining incoming traffic and blocking malicious requests based on predefined security rules. They can also help reduce the risk of zero-day attacks, as they provide an additional layer of protection that may catch unknown vulnerabilities.
8. Regularly Backup Your Data
Even with the best security measures in place, data loss can still happen. Ransomware attacks, hardware failures, and other unforeseen issues can lead to the loss of critical application data. To mitigate this risk, make regular backups of your application data and store them securely.
Test your backups regularly to ensure they can be restored quickly in the event of an attack. Having a solid backup and disaster recovery plan can help you recover your application and minimize downtime in case of a security breach.
9. Conduct Security Audits and Penetration Testing
To ensure that your web application is secure, it’s important to perform regular security audits and penetration testing. A security audit will assess the overall security posture of your application, including code reviews, infrastructure assessments, and configuration checks.
Penetration testing, or ethical hacking, involves simulating an attack to identify vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them. By conducting these tests regularly, you can identify weaknesses and patch them before they become a problem.
Conclusion
Securing your web application is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, expertise, and the adoption of best practices. By implementing strong authentication, keeping software up to date, sanitizing input, and using tools like WAFs and encryption, you can protect your application from a variety of threats and ensure a safe experience for your users.
If you're looking to create a secure and robust web application, partnering with a web application development company can help ensure that security is embedded into your application from the start. Their expertise in building secure, scalable solutions can help you avoid common pitfalls and provide the protection your users expect.
0 notes